Bitcoin and Ethereum
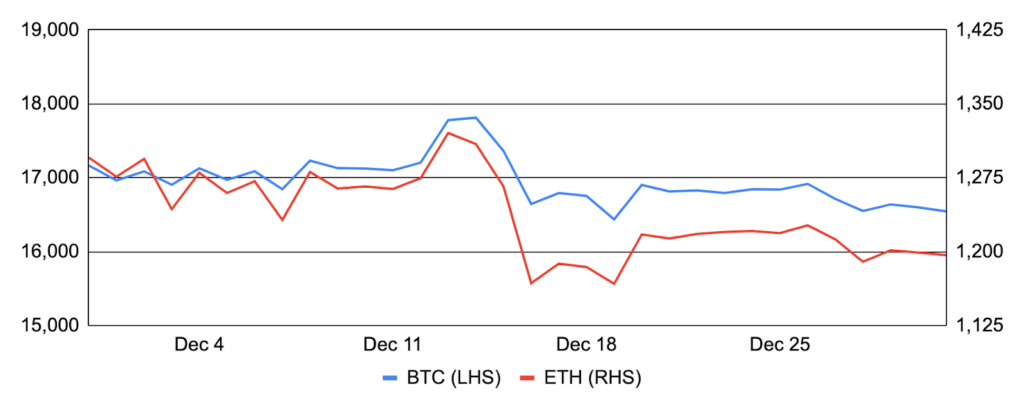
Bitcoin continued in its trend downwards in December, falling ~4% after entering the month around $17,200 and finishing at $16,500. Much of the price action occurred during the news-heavy week of the 12th that featured numerous inflation releases and central bank policy decisions across the globe. Bitcoin rallied at the beginning of the week behind a better-than-expected U.S. CPI print, but soon reversed lower as expectations for a higher-for-longer interest rate policy regime heightened recessionary fears. Outside of this macro-heavy week, bitcoin was relatively steady and Bitcoin-specific news was light. Mining difficulty had its largest downward adjustment since China’s crackdown on mining in 2021, but the backdrop remains incredibly challenging. Core Scientific, the largest Bitcoin miner by hashrate, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy, Greenidge Generation noted that its continued viability is in ‘substantial doubt’, and Argo, which has similarly flagged its own bankruptcy concerns in recent months, sold its flagship Helios mining facility to Galaxy Digital to remain afloat. Elsewhere, a record 66%+ of the total bitcoin supply hasn’t moved in over a year; CoinCorner and Bitnob enabled cross-border payments in multiple fiat currencies via The Lightning Network; and, on-chain sleuth ZachXBT flagged ~$1.7m of bitcoin that moved from previously dormant wallets tied to the defunct crypto exchange QuadrigaCX.
Ethereum fared worse than bitcoin, falling ~8% during the month after entering at ~$1,300 and finishing around ~$1,200. Muted on-chain activity reversed ETH’s deflationary trend observed in recent months, and net ETH issuance totaled ~4,800 in December. Ethereum’s All Core Devs (ACD) call during the month was particularly notable, as it established the scope for the Shanghai hard fork expected in March 2023. Shanghai’s key focus is to enable withdrawals of staked ETH, which is currently illiquid and cannot be withdrawn from validator accounts. Shanghai also aims to upgrade the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) via a series of EIPs collectively known as EVM Object Format (EOF), but some of these may be dropped if client teams fail to implement them before January 5th to avoid delaying withdrawals. Somewhat contentiously, the first step in Ethereum’s sharding roadmap known as Proto-danksharding that aims to decrease L1 data costs to scale throughput via L2 rollups was left out of Shanghai and it will now be the cornerstone EIP in the subsequent Cancun hard fork. In other Ethereum-related news, the percentage of OFAC-compliant Ethereum blocks began falling from its November peak (covered more here); BitMEX introduced the first ETH staking yield swap; ConsenSys launched its zkEVM private testnet; Visa authored a paper exploring how account abstraction on Ethereum could support auto payments for non-custodial wallets; Solana’s top NFT project DeGods announced it will bridge to Ethereum in 1Q23; and, Vitalik Buterin published a blog post discussing what excites him in Ethereum’s application ecosystem.
BTC and ETH
Source: Santiment, GSR
Criminal Enforcement
December was a busy month for the Justice Department as federal officials scrambled to respond to the rampant fraud effectuated by FTX and Alameda, covered at length in our November commentary. Most prominent was the arrest of Sam Bankman-Fried (SBF) on December 12th by Bahamian authorities at the request of the U.S. government based on a sealed criminal indictment filed by the Southern District of New York. Notably, the arrest occurred just one day before SBF was expected to provide virtual testimony on the collapse of FTX before the House Financial Services Committee. SBF’s charges were elucidated the next day as the indictment was unsealed, and they include wire fraud and several conspiracy to commit charges including wire, securities, and commodities fraud, money laundering, and campaign finance violations. The SEC and CFTC further tacked on civil charges of their own. SBF was later extradited to the U.S. and released on a reportedly unprecedented $250m bail bond while awaiting trial. The terms of SBF’s release were controversial as he wasn’t released on a conventional bail bond but on a personal recognizance bond that essentially amounts to a promise that he would pay the court $250m should he fail to show up for trial. Cash collateral was not required to secure his release, and the only collateral posted was his parents house that is estimated to be worth less than 2% of the total bond.
To make matters worse for SBF, his inner circle quickly turned against him and began to cooperate with authorities. The DoJ unsealed the guilty pleas of former Alameda Research CEO Caroline Ellison and FTX co-founder and former CTO Gary Wang to charges arising from their participation in schemes to defraud FTX customers and investors. Caroline’s unsealed plea deal confirmed she was facing a maximum total sentence of 110 years initially, but all charges except criminal tax violations will be waived if she fully cooperates with the terms outlined in the deal.
Amidst the theme of criminal enforcement, we’d be remiss not to mention that Avi Eisenberg, the individual behind October’s Mango Markets exploit, was arrested by the FBI on charges of market manipulation. While much still remains to be seen, many have speculated that the case may provide important industry precedent.
U.S. Department of Justice Announces Charges Against SBF

Source: Justice.gov, GSR
Protocol Developments
Though it was a generally quiet month from a crypto price perspective, protocol upgrades were anything but, with several prominent deployments over the period. Avalanche released Banff 5 to introduce its Avalanche Warp Messaging communication protocol that allows subnets to communicate and share data directly with one another. Gnosis Chain successfully switched its consensus mechanism from proof-of-authority to proof-of-stake in a process similar to Ethereum’s Merge. And DEX aggregator 1inch launched its Fusion upgrade to improve on cost efficiency and security.
In addition, decentralized oracle network Chainlink launched the beta version (v0.1) of its long-awaited staking program, a cornerstone of its Chainlink 2.0 roadmap. The goal of Chainlink staking is to give ecosystem participants the ability to increase security guarantees and user assurances of oracle services by backing them with staked LINK, which can be slashed and redistributed if the services delivered fail to meet the criteria outlined in the on-chain service-level agreement (SLA). Native token emissions will create a base level of rewards to bootstrap staking initially, but it’s believed that inflationary rewards will be tapered through time as oracle use increases and more organic fee revenue can be directed to stakers. Lastly, stake creates additional differentiation between node operators with similar historical reliability metrics (i.e., response time, accuracy, etc.). Chainlink staking is being shipped iteratively, with many aspects of the staking roadmap withheld from the currently deployed beta implementation (i.e., slashing, user fee rewards, etc.). The initial beta release prioritizes the deployment of a reputation framework and alerting system, which is a prerequisite for the introduction of slashing as stakers must be able to flag a breach of an SLA and be compensated for doing so. Chainlink staking is currently confined to the ETH/USD price feed on Ethereum mainnet, and the total amount of staked LINK is capped at 25m for now. While the cap is intended to be raised to 75m in the coming months, LINK staking demand has far exceeded the cap, and the staking pool was filled to capacity within a few hours of the general access launch on December 8th.
Chainlink’s Staking Roadmap
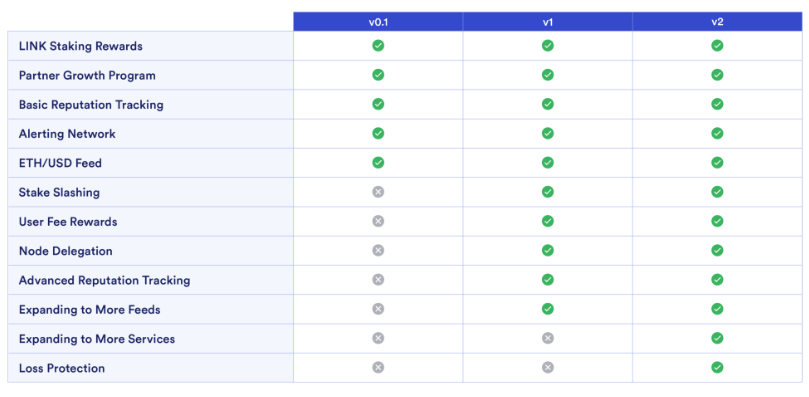
Source: Chainlink, GSR. v0.1 launched in December.
Macro and Monetary Policy – Japan’s Reversal
Inflation in the U.S. came in lower than expected in November, which sparked a brief resumption of risk appetite. Headline CPI rose 7.1% year-over-year, a decline from +7.7% the month before and better than the +7.3% consensus. U.K. and Eurozone inflation data followed, with growth decelerating from prior months and potentially signaling that inflation in Europe has peaked. The FOMC met mid-month, with the Federal Reserve hiking interest rates by just 50 bps, though Chairman Powell’s post-meeting commentary struck a hawkish tone, emphasizing that rates will likely remain at higher levels for longer. Numerous other central banks such as the Bank of England, the European Central Bank, the Bank of Canada, the Swiss National Bank, and the Reserve Bank of Australia also hiked rates, each by 35 to 50 bps and in line with their respective forecasts.
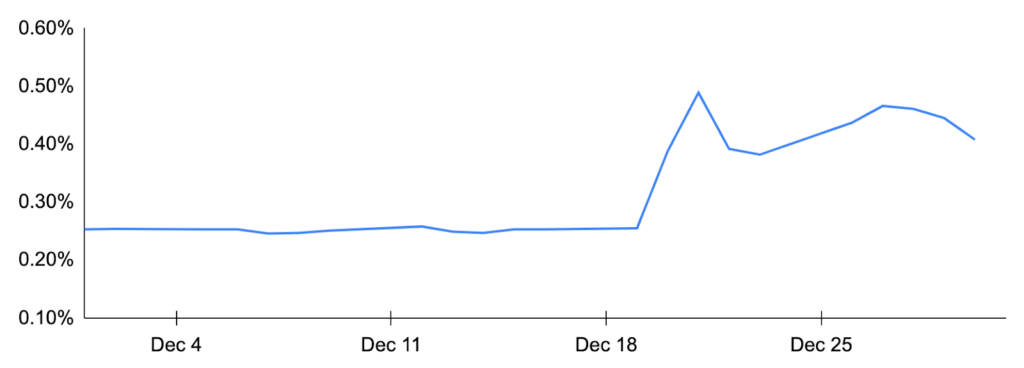
Unlike other developed market central banks, the Bank of Japan (BoJ) has maintained loose monetary policy, keeping short-term interest rates negative as other countries continue raising rates. While the BoJ kept short-term interest rates flat at -10 bps during the month, the country’s monetary authority surprised markets as it adjusted it’s yield curve control (YCC) program by widening the range it allows the 10-year yield to fluctuate around its 0% target, increasing the range from 25 to 50 bps. Japanese government bonds sold off and the yen rallied versus the dollar in response. While the BoJ claimed the move is not a departure from its loose monetary policy, some market participants viewed the move as the first step towards tightening and policy normalization that may commence after Governor Kuroda steps down in April 2023.
10-Year Japanese Government Bond Yield
Source: CNBC, GSR
GSR in the Media
- The Block – Crypto trading firm GSR sees opportunities in Alameda’s demise
- The Block – Digital Currency Group tokens red across board, sparking market speculation
- The Block – Crypto has the highest ‘talent density’ since the internet’s early days, says GSR CEO
- CoinDesk – Bitcoin’s Stagnant Crypto Dominance Points to Investor Exodus After FTX Bankruptcy
- CoinDesk – Crypto Options Exchange Deribit Registered Record Trading Volume in November
- Fox Business – Maxine Waters seems to have a ‘soft spot’ for Sam Bankman-Fried: Rich Rosenblum
- The Information – The DeFi Conundrum: Why Crypto Exchanges Like Uniswap Are Struggling to Reach Critical Mass — The Information
- Yahoo! Finance – The cryptocurrencies that held up the best in 2022
Authors:
Matt Kunke, Junior Strategist | Twitter, Telegram, LinkedIn
Brian Rudick, Senior Strategist | Twitter, Telegram, LinkedIn
View December 2022 Market Update
Disclaimers
This material is provided by GSR (the “Firm”) solely for informational purposes, is intended only for sophisticated, institutional investors and does not constitute an offer or commitment, a solicitation of an offer or commitment, or any advice or recommendation, to enter into or conclude any transaction (whether on the terms shown or otherwise), or to provide investment services in any state or country where such an offer or solicitation or provision would be illegal. The Firm is not and does not act as an advisor or fiduciary in providing this material.
This material is not a research report, and not subject to any of the independence and disclosure standards applicable to research reports prepared pursuant to FINRA or CFTC research rules. This material is not independent of the Firm’s proprietary interests, which may conflict with the interests of any counterparty of the Firm. The Firm trades instruments discussed in this material for its own account, may trade contrary to the views expressed in this material, and may have positions in other related instruments.
Information contained herein is based on sources considered to be reliable, but is not guaranteed to be accurate or complete. Any opinions or estimates expressed herein reflect a judgment made by the author(s) as of the date of publication, and are subject to change without notice. Trading and investing in digital assets involves significant risks including price volatility and illiquidity and may not be suitable for all investors. The Firm is not liable whatsoever for any direct or consequential loss arising from the use of this material. Copyright of this material belongs to GSR. Neither this material nor any copy thereof may be taken, reproduced or redistributed, directly or indirectly, without prior written permission of GSR.